Quick & Easy Process for Getting a Food Handler Certificate in Toronto
In a dynamic and culturally rich city like Toronto, the food industry plays an integral role in everyday life. From busy restaurants and food trucks to school dining rooms and catering operations, the need for Food Handler Certificate in Toronto and adhering to safe food handling procedures has never been greater.
The Food Handler Certificate in Toronto is important to this role, and it is required for anybody who prepares, stores, or serves food.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the importance of food handler certification in Toronto, who needs it, and how to obtain it quickly and easily. So without further ado, let’s get started.
What is a Food Handler Certificate in Toronto?
A Food Handler Certificate, often known as a Food Safety Certificate in Toronto, is a formal credential presented to individuals who complete a provincially certified food safety training program and test.
The certificate verifies that the individual has learned to handle food properly and avoid foodborne illness. To receive a Food Handler Certificate in Toronto, food handlers must complete an Ontario-approved course.
Who Needs a Food Handler Certificate in Toronto?
It is recommended by Toronto Public Health that any person who is engaged in the preparation, storage, handling, or serving of food in a commercial environment should hold a valid Food Handlers Certificate in Toronto. This includes:
- Line cooks and chefs
- Kitchen assistants and prep cooks
- Food truck operators and street vendors
- Catering staff and banquet servers
- Restaurant owners and managers
- Convenience store staff handling open food
- Staff in cafeterias, schools, and hospitals
- Grocery store and bakery employees
Toronto or any other municipality in Ontario demands that at least one certified food handler be present on-site in any food premises during every hour of business
What this implies is that although you might not necessarily handle food all the time, being certified can help you to become a better worker as well as increase the level of workplace safety.
Why the Food Handlers Certificate Matters in Toronto
Food service is more than a business, it’s a cornerstone of public health. Poor food handling has serious consequences, such as cross-contamination, food poisoning, or large-scale outbreaks of foodborne illness. A Food handler certificate in Toronto ensures that food service workers have been educated in the science and best practices of food safety.
Here’s why Toronto Food Safety training is critical:
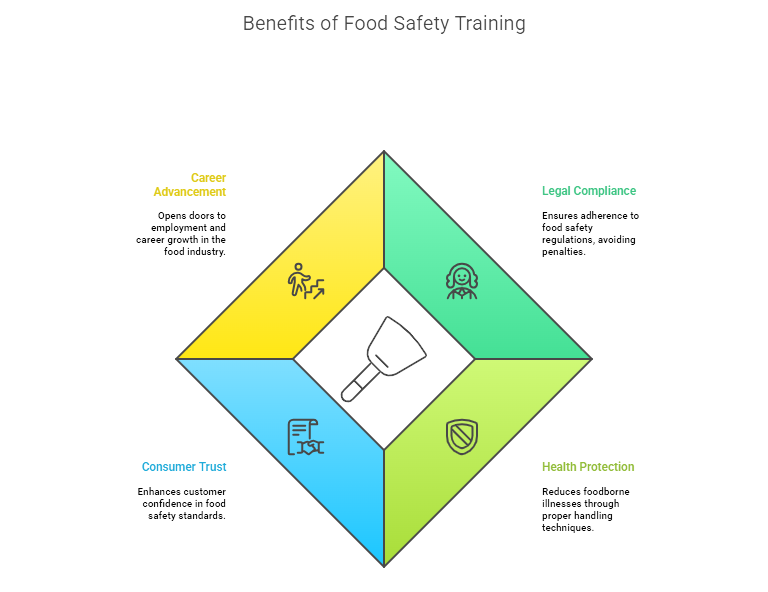
- Lawful Obligation: Certification ensures your business is following local and provincial food safety regulations and helps minimize the risk of non-compliance during an inspection by Toronto Public Health.
- Lower Foodborne Illness Risk: Certified food handlers learn about hazards and methods of controlling contamination and food safety procedures, which reduces foodborne illness risk.
- Greater Consumer Confidence: Consumers tend to trust businesses that adhere to high standards of food safety, and certified individuals can reaffirm this confidence.
- Professional Growth: Holding a valid Food Handler Certificate broadens opportunities for employment and may be necessary for advancement opportunities in the food sector.
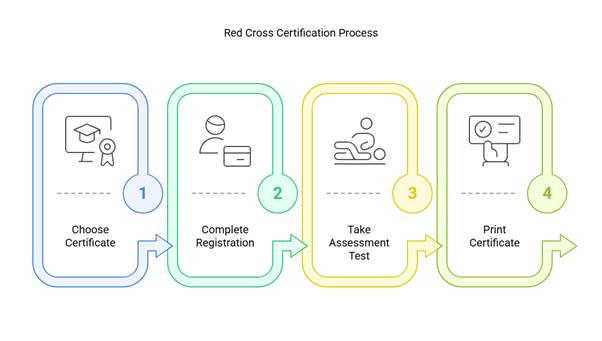
How to Get Certified in Toronto
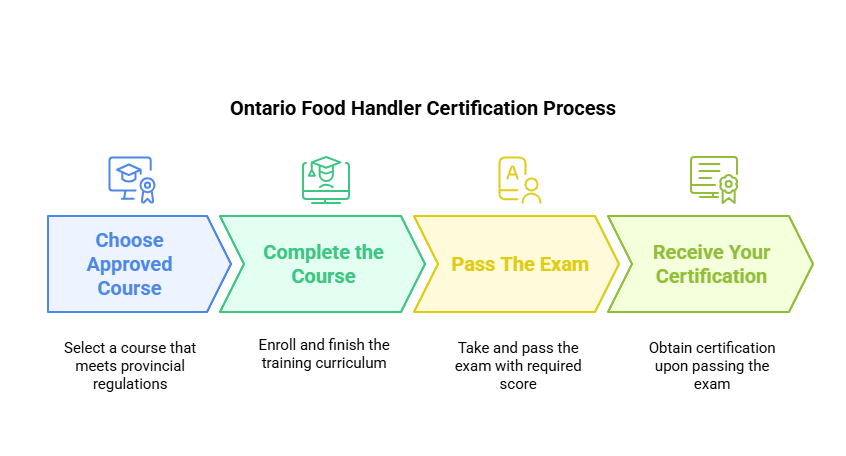
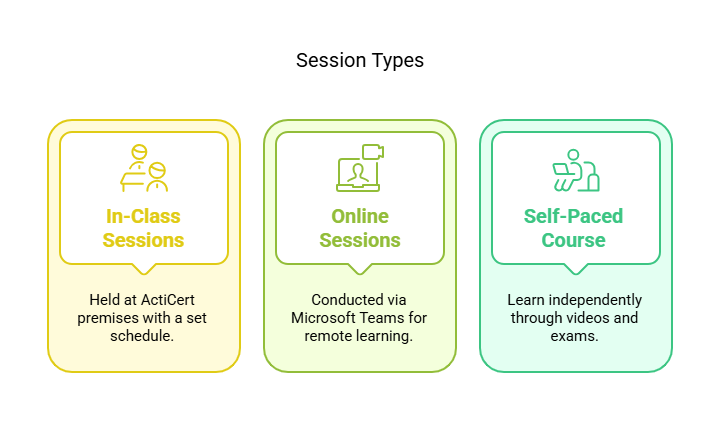
Getting your Food Handler Certificate in Toronto is a simple, step-by-step process when you choose the right provider. ActiCert Inc. is listed as a recognized provider for both in-class and online modules of the approved food handlers certificate program.
Below is a step-by-step procedure:
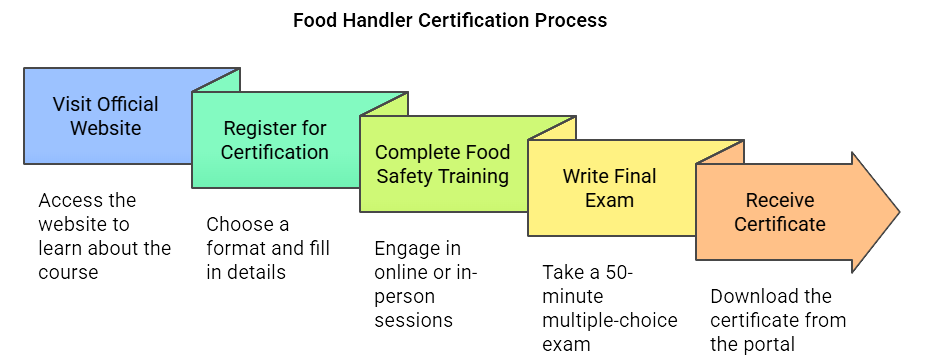
1. Visit the Official Website
Getting to know about the course is as important as getting a Toronto food handler certificate. Visit ActiCert’s official website at https://acticert.com/food-handler-certificate/ to learn about the certification and its course modules.
2. Register for the Certification
Choose the format you wish to register for. Acticert provides in-class instructor-led and online instructor-led sessions. Select what best suits your schedule. Go to the registration page and fill in the basic details to get started. Here’s a quick link for you: https://acticert.com/food-handler-certification-registration/
3. Complete the Food Safety Training, Toronto
You can take the course online at your own pace or choose in-person sessions. The curriculum includes:
- Foodborne Illness and Food Contamination (Sources and Prevention)
- Basic Microbiology and Factors Affecting Microbial Growth
- Food Safety Management
- Time/Temperature Controls for Potentially Hazardous Foods
- Displaying, Serving/Dispensing, and Discarding
- Facility, Equipment, Receiving, and Storage of Food
- Cleaning, Sanitization, and Personal Hygiene
4. Write the Final Exam
The exam will be held following the instruction sessions. It is 50 minutes long and has 50 multiple-choice questions. A passing score of 35 out of 50 (70%) is required to obtain the Food Handler Certificate in Toronto.
5. Receive Your Certificate
Successful students will receive a certificate immediately after passing the exam. The final food handlers certificate will be accessible for download through the e-learning portal, where the final evaluation will be completed.
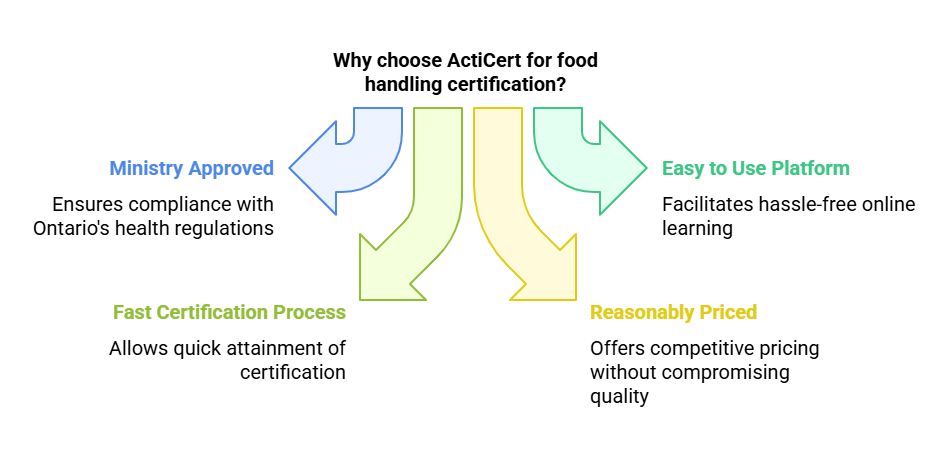
Why Choose ActiCert for Certification?
Although there are various training providers in Toronto, ActiCert is recognized for being easy to use, offering rapid certification, and compliance with Toronto Public Health standards.
The following are the reasons why ActiCert’s Food Handler Certificate in Toronto stands out:
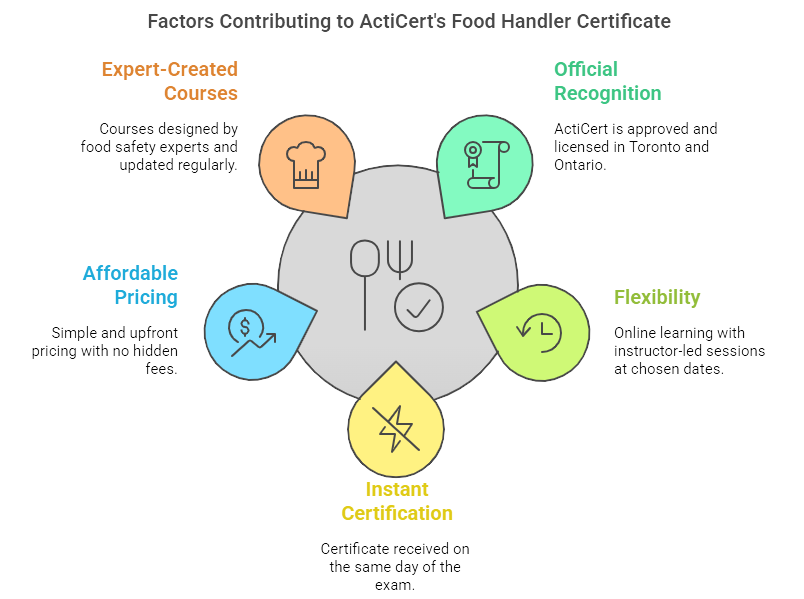
- Officially Recognized: ActiCert is an approved and licensed training provider whose certification is acceptable in Toronto and other provinces of Ontario.
- Fast, Flexible, and Convenient: Learn online with instructor-led sessions on a chosen date per your availability.
- Instant Certification: Pass your exam and receive your certificate the same day, which is ideal for individuals who need quick certification to perform their job.
- Affordable Pricing: Simple, upfront pricing with no surprise fees.
- Expert-Created: Courses are created by seasoned food safety experts and are updated continually to incorporate current health requirements.
Highlights of the ActiCert Course
When you enroll in ActiCert’s Food Handler Course Toronto, you get:
- 1-day course available in online and in-class formats
- In-depth knowledge of food safety and food handling practices
- Training from experienced professionals from the food industry, fully qualified to deliver the standardized, ministry-approved course
- Accommodations for special needs, if any
- A maximum of two attempts to pass the examination
- Immediate certification upon exam completion on the e-portal
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can I take the training from my home in Toronto?
Yes. ActiCert offers the option of choosing between the online and in-person class formats. With online instructor-led sessions, you can completely attend the course from the comfort of your home, no classroom needed.
2. What are the prerequisites required for registration?
Anyone 18 years of age or older can register for the course, as no prior qualifications are required. Just a basic level of English literacy is required, as our course is available in English.
3. How long is the Food Handler Certificate in Toronto valid?
The food handlers certificate in Toronto is valid for 5 years in Toronto and all of Ontario.
4. Is this certification of any value to get a job in Toronto?
Yes! A food handler certificate in Toronto is often required to work in food establishments across the Greater Toronto Area (GTA).
5. How much salary does a food safety worker get in Toronto?
The approximate food safety salary in Toronto ranges from $40k – $60k per year. Entry-level positions start at $30k per year, while most experienced workers make up to $100k per year.
Final Thoughts
Maintaining strong food safety standards in Toronto’s diverse and fast-paced food business is more than just passing inspections; it’s also about safeguarding public health, earning customer trust, and advancing your career. Obtaining a Food Handler Certificate in Toronto is a legally and ethically sound step toward reaching those objectives.
With ActiCert, it is smooth, cost-effective, and accessible from anywhere. Whether you are an individual who wants to begin your journey in the food industry or a company that wants to certify your whole team, ActiCert provides a fast and simple solution that does not compromise on quality.
Enroll with ActiCert today at +1 (905) 487 7043 and get certified with confidence. For further assistance, feel free to send us your queries at foodsafety@acticert.com.